This post is adapted from a paper that was published in the Journal of Procedia Engineering, Volume 107, 2015, Pages 463-469 and in the 2015 Conference on Humanitarian Technology: Science, Systems and Global Impact Conference (HumTech). The complete paper is available here (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877705815010577).
Considering the large number of mobile subscribers and the growing market in Africa, local developers and entrepreneurs with the right set of skills have an important role to play in the creation of mobile services solving local problems in health, education, agriculture, and citizen participation. Who is/will training/train them? Where will they learn? Very few multi-year capacity building initiatives on mobile technology exist in the region. Incubators often do not have this type of offering. Universities are too slow in changing their curriculum. MOOC courses did not disrupt education as expected. Competitions and hackathons organized by corporations and other institutions are good ways to learn technologies but their focus is too narrow. To think further ahead, it is important to wonder: Who will teach the next technologies? Wearable? Internet of Things? Blockchain? Etc.
MobileSenegal
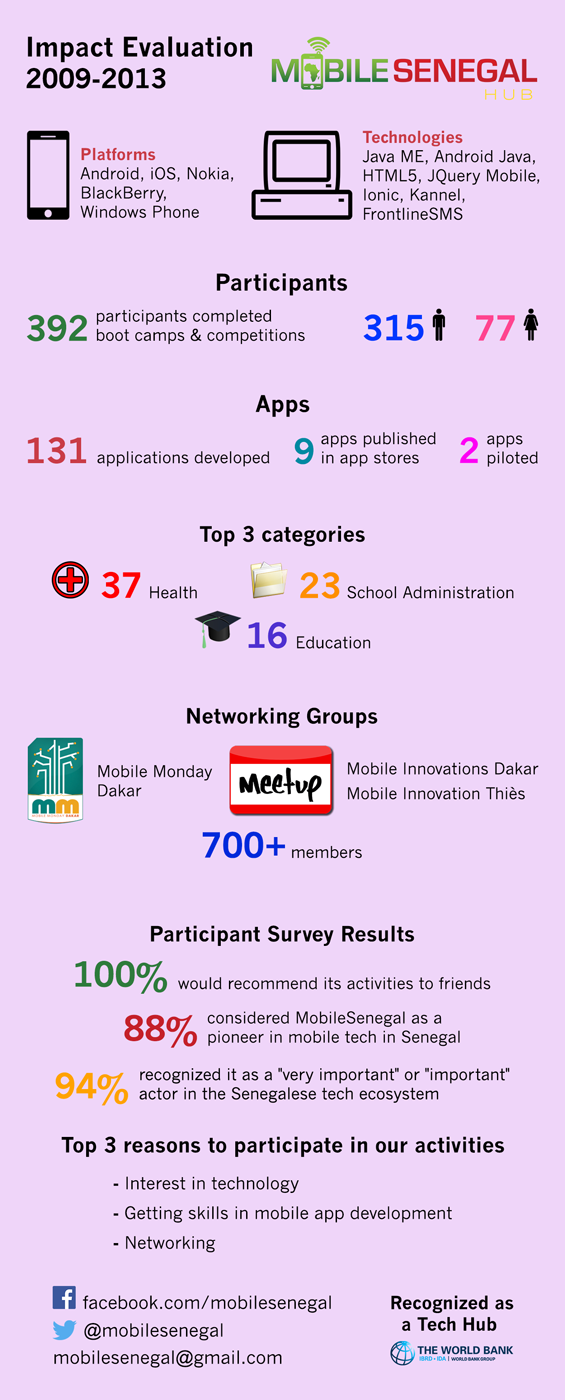
We have been working in Senegal since 2008 through the MobileSenegal project (http://mobilesenegal.org) to build capacity in mobile technology. We witnessed the changes and evolved our offering. We take a holistic approach and favor intensive training sessions focusing on technical, design, soft, software engineering, and entrepreneurship skills. Our training emphasizes project-based learning. We rely on the support of an active ecosystem that we gather in two meetup groups: Mobile Innovations Dakar (http://www.meetup.com/mobileinnovationsdakar) and Mobile Monday Dakar (http://mobilemondaydakar.org). 131 mobile apps were developed by 392 participants (296 males and 71 females) in boot camps, courses and competitions between 2009 and 2013.
Study
What is the impact of MobileSenegal? We administered a survey that was sent to actors of the tech ecosystem. 163 participants to our activities answered the survey (45 complete answers). We systematically analyzed the mobile solutions that were designed throughout the years (between 2009 and 2013).
Impact on participants and the community
Our findings show that participants are trained with skills that are valuable in the Senegalese job market and MobileSenegal responds to a specific need in the Senegalese tech ecosystem that is not covered by other initiatives.
- Participants would recommend its activities to friends (100%).
- Participants were very satisfied with the activities of MobileSenegal and considered it as a pioneer in mobile in Senegal (87.7%).
- MobileSenegal is perceived as very important (40.8%) and important (53%) in the Senegalese tech ecosystem due to the role of mobile technology in Africa, its focus on mobile for development (M4D), and the importance it gives to training faculty.
- Participants cited interest in technology (19.9%), getting skills in mobile app development (17.7%) and networking (14.4%) as the main reasons to participate in MobileSenegal activities.
- Participants felt that the skills they acquired helped them strengthen their CV (25%) and get an internship (16.4%), ignited their interest in mobile and entrepreneurship (22.4%), and supported their day-to-day job (8.6%).
- Their skills permitted them to secure internships and employment in the most recognized startups and companies (e.g., WARI, Money Express and Ferlo, ARTP, Orange, Tigo, People Input, etc.).
The apps
Only 9 apps were released in Nokia Store and Google Play and 2 apps were piloted in Senegal (out of 131) after mentoring from MobileSenegal. Participants mentioned that time deficiency, studies, and impossibility of registering for a developer account without a credit card were reasons that kept them from publishing their apps. In addition, as explained earlier, publishing an app was not one of their priorities when participating in activities.
Apps proposed by participants mainly focused on Health (37), School Administration (23) and Education (16).
- Most of the health apps were health education apps with content on maternal health, blood donation, vaccine, malaria and diabetes, apps that improve communication between doctors and patients, and information on health facilities.
- School administration apps reflected on the everyday life of Senegalese students and some of their important and urgent concerns (e.g, grades, campus dining/housing).
- Education apps focused on quizzes and study guides for children to learn numbers and letters, and apps to learn about Africa, the environment and Wolof.
What’s next?
We are currently looking at new models to sustain our initiative though intensive training of instructors, and new models of teaching to accelerate the release of enterprise and consumer mobile applications and train more participants at once. Stay tuned! Great things are coming!
Authors: Christelle Scharff, Chun Hei Cheung, Jean-Marie Preira
Acknowledgement
We thank all the participants of MobileSenegal activities for their involvement and feedback. We are particularly grateful to Amdane Samb and Landry Ahouansou for their work. We also thank our sponsors since 2009: VentureWell (ex-NCIIA), Google, IBM, WARC (West African Research Center), and Neurotech.